Stargazing is a magnificent adventure that connects us with the universe and deepens our understanding of celestial wonders. For beginners eager to embark on this journey, knowing how to observe stars effectively can transform a simple night under the sky into a memorable experience filled with awe and discovery. Whether you are gazing at the moon, recognizing constellations, or tracking planetary movements, the thrill of observing stars can ignite a passion for astronomy that lasts a lifetime.
To make the most of your stargazing experience, it is essential to be equipped with the right knowledge and tools. The vast expanse of the night sky can initially feel overwhelming, but with the right tips and techniques, anyone can learn to distinguish between the twinkling stars and other celestial objects. Understanding factors such as location, weather conditions, and timing will greatly enhance your ability to observe stars. As you immerse yourself in this fascinating hobby, you might find yourself inspired to learn more about the science behind the stars, including their formation and significance in our universe.
In this guide, we will explore practical tips for effective stargazing, tailored specifically for beginners. By following these suggestions, you will not only enhance your skills in observing stars but also cultivate a deeper appreciation for the wonders of the night sky. Whether you're peering through a telescope or simply enjoying the beauty of the stars with the naked eye, let's delve into the captivating world of stargazing and unlock the secrets that lie beyond our planet.

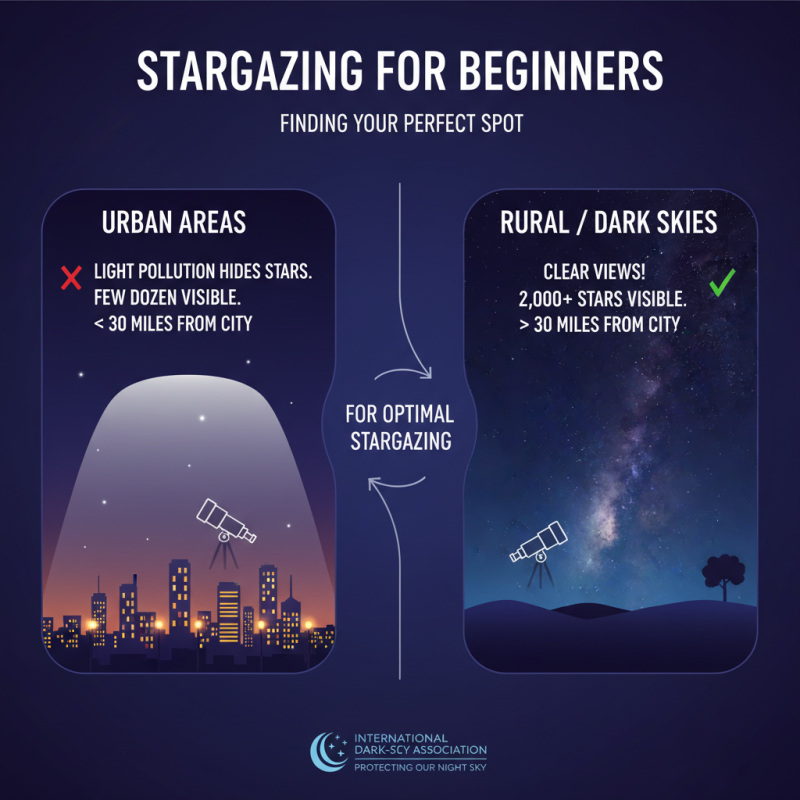
Choosing the right location for stargazing is crucial for beginners who wish to enjoy the beauty of the night sky. According to the International Dark-Sky Association, light pollution is a significant barrier to optimal stargazing, diminishing the visibility of celestial objects. It is recommended to seek out areas that are at least 30 miles away from urban centers, as studies indicate that ow regions with dark skies can reveal thousands more stars compared to brightly lit urban areas. Urban light pollution can decrease visibility to only a few dozen stars, while dark rural skies can offer views of 2,000 stars or more.
Furthermore, several factors contribute to an ideal stargazing location. Elevation plays a vital role; higher altitudes reduce the amount of atmosphere one must look through, thereby enhancing clarity. The U.S. Geological Survey emphasizes that stargazers would benefit from selecting locations on elevated terrains, which not only offer clearer views but also are often less affected by atmospheric disturbances. Additionally, selecting nights with stable weather conditions, away from fog or clouds, is essential for an optimal experience, as clear skies significantly improve visibility. According to meteorological data, choosing nights with minimal humidity and low wind can enhance visibility of celestial phenomena, making your stargazing adventure all the more rewarding.
Stargazing is a captivating hobby that can deepen one's appreciation for the universe, and having the right gear is essential for beginners. A quality telescope can significantly enhance the experience, allowing you to observe celestial details that are invisible to the naked eye. According to a survey conducted by the American Astronomical Society, about 75% of novice astronomers found that having a telescope improved their stargazing experience, as it enabled them to explore planets, nebulae, and star clusters more effectively.
In addition to a telescope, binoculars are a portable and user-friendly option for beginners. They provide a wider field of view and are perfect for spotting constellations, as they can reveal stars that are too faint to see without optical aid. Research indicates that nearly 40% of stargazers prefer using binoculars, especially when starting, due to their ease of use and affordability. Furthermore, a star chart or stargazing app can assist in navigating the night sky, helping beginners identify constellations and celestial events with guidance tailored to their geographical location and time of year. Preparing with these essential tools can transform the stargazing experience, making it more enjoyable and educational.
Understanding basic astronomy terminology is essential for beginners wanting to delve into the vastness of the night sky. Familiarizing oneself with terms such as "constellation," "light-year," and "magnitude" can greatly enhance the stargazing experience. A constellation refers to a recognizable pattern formed by stars that we can identify in the sky, often rooted in mythology and history. Learning specific constellations, like Orion or Ursa Major, can provide a guidepost for navigating the night sky.
Another important term is "light-year," which measures the distance that light travels in one year, roughly 5.88 trillion miles. This unit helps astronomers convey vast distances between celestial objects, emphasizing just how expansive our universe is. Additionally, understanding "magnitude" is crucial for assessing the brightness of stars—this can determine which stars are observable with the naked eye and which require telescopes. Together, these terms lay the groundwork for a more fulfilling and informed stargazing experience, allowing beginners to appreciate the cosmic wonders above them with confidence and curiosity.
Identifying stars and constellations can be a fascinating endeavor for stargazing beginners. A study by the International Astronomical Union indicates that there are over 88 officially recognized constellations in the night sky. For newcomers, familiarizing oneself with a few key constellations can make the experience all the more rewarding. A great starting point is the Orion constellation, which is easily recognizable due to its prominent belt formed by three bright stars: Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka. Learning these foundational shapes can greatly enhance one's ability to navigate the sky.
Using resources such as star charts or mobile apps can further aid in identifying stars and constellations. Research published in the Journal of Astronomy Education reveals that interactive resources can improve observational skills by up to 40% among beginners. Additionally, understanding the seasonal changes in visibility can help enthusiasts plan their stargazing sessions effectively. For example, constellations like Ursa Major, which includes the famous Big Dipper, are prominent in northern skies, especially during the summer months. By observing specific stars and their positions relative to one another, beginners can develop a deeper appreciation for celestial navigation and the stories woven into constellations throughout human history.
Stargazing is a delightful activity that allows us to connect with the universe, and understanding the optimal conditions for viewing the night sky is crucial for beginners. Research indicates that the best time for stargazing is during the months of late fall to early spring. During these months, the Earth’s tilt offers clear and crisp nights, minimizing atmospheric disturbances. The absence of humidity and cloud cover enhances visibility, allowing stargazers to enjoy celestial phenomena such as meteor showers and planetary alignments. According to the International Dark-Sky Association, light pollution is a significant barrier for optimal stargazing, suggesting that choosing a location away from urban lights significantly improves the quality of what can be seen.
Moreover, the impact of weather on stargazing cannot be overstated. Ideal conditions include temperatures that are neither too hot nor too cold, as extreme temperatures can disturb air layers and degrade visibility. The best nights are often those following a rainfall when the air is fresh and the sky is clear. Studies show that approximately 80% of people live under light-polluted skies, emphasizing the importance of planning for moon phases as well; a new moon provides the darkest skies. Aligning your stargazing adventures with these optimal weather conditions and timing can greatly enhance your ability to observe stars and celestial events effectively.






